Sickle Cell Disease
Sickle cell disease is an inherited blood disorder that affects red blood cells. It is a type of hereditary haemoglobin disorder where valine has been substituted for glutamic acid at position 6 of haem beta chain, caused by a point mutation. You must remember that Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is inherited in a Mendelian recessive manner. Therefore patients with two Sickle genes (SS) or carry one S gene but with concomitant Beta Thalassemia ( SB) are affected.

This disease is common in peoples of Equatorial African ancestry.
Clinical Presentations
Remember that all clinical features are due to two main features of the disease- haemolysis and vaso-occlusive crisis. You must understand that HbS is insoluble in the dexoygenised form and they have a shorter life span due to increased fragility, therefore causing chronic haemolysis ( similar to Thalassemia). The red blood cells with HbS also tend to aggregrate and cause thrombosis, this will leads to tissue infarction. Remember that the vaso-occlusive crisis tends to be precipitated by HADI ( hypoxia, acidosis,dehydration and infection)
Clinical features due to haemolysis
Anemia
Gallstone
Bone marrow enlargement
( these features also occur in Thalassemia patients)
Clinical fatures due to vaso-occlusive crisis
Bone pain- may cause vascular necrosis
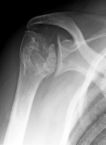 Humerol head avscular necrosis
Humerol head avscular necrosis
Leg ulcers
Genito-urinary- priapism
Cerebral-stroke
Spleen- initially may cause splenomegaly due to extra medullary haemopoiesis ( due to anemia) but later splenic infarct and hyposplenism. Patients tend to have capsulated bacteria infection and Salmonella osteomyelitis.
Chest-acute chest pain
( remember that these are all due to thrombotic events)
Physical Signs
Patients tend to be pale with jaundice. Hepatomegaly may be present. Look for chronic leg ulcers.
Investigations
Full blood count- low Hb with features suggesting haemolysis such as increased reticulocyte counts
LFT- increased bilirubin and AST
Peripheral blood film- sickled cells
Haemoglobin electrophoresis- to determine variant haemoglobin
X-ray- to look for vascular necrosis if patients present with joint pain.
Management
During sickle crisis ( oxygen, analgesia, rehydration)
Long term management
- prophylactic penicillin for prevention of penumococcal infection,
- management of anemia, however be careful about secondary iron overload due to multiple transfusions
- folate supplements
Tips for MRCP
1) Always suspect Sickle Cell Disease if a patient has anemia and chronic leg ulcers.

1 comment:
NICOSAN for the Treatment of Sickle Cell Disease
There is a relatively new treatment for sickle cell being
produced in Nigeria by an American company called NICOSAN®,
it's proprietary name is NIPRISAN® . It was developed on
the premise of traditional Nigerian plant based medicinal
practices for the treatment of sickle cell disease.
It has been tested through phase IIb clinical trials and
found to be highly efficacious. Phase III trials have yet
to be completed however it was approved for sale in Nigeria
based on phase IIb trials and toxicity studies which showed
it to be safe and non-toxic.
Double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomised cross-over
clinical trial of NIPRISAN® in patients with Sickle Cell
Disorder
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B7GVW-4DS346T-1S&_user=10&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=211981d545303693affebb8c012d2cac
Efficacy of Niprisan in the prophylactic management of
patients with sickle cell disease
http://www.sciencedirect.com/science?_ob=ArticleURL&_udi=B6VS8-43DFJCH-G&_user=10&_rdoc=1&_fmt=&_orig=search&_sort=d&view=c&_acct=C000050221&_version=1&_urlVersion=0&_userid=10&md5=10528ecbab3ec7e977301fb9f2688ef6
NIPRISAN -- Nix-0699 Toxicity Studies
http://www.biospace.com/news_story.aspx?StoryID=15890720&full=1
Niprisan (Nix-0699) improves the survival rates of
transgenic sickle cell mice under acute severe hypoxic
conditions
http://www.blackwell-synergy.com/doi/abs/10.1046/j.1365-2141.2003.04536.x?journalCode=bjh
NIPRISAN Case, Nigeria
A Report for GenBenefit (2007)
http://www.theparliament.com/NR/rdonlyres/F46A1A12-0A1A-41DA-9F5D-A11486CA9BFA/0/Nigerian_Case.pdf
This drug is a major advancement in the treatment of sickle
cell disease unfortunately it is not available in the U.S..
Although the compound has been granted orphan drug status
by the FDA and the regulatory body of the European Union,
to date investigational drug applications for the approval
process have yet to be submitted. Getting a drug approved
in either area is extremely expensive. Until there is
funding available to proceed with the FDA and EU
applications it will be difficult for non-Nigerians to
obtain the drug.
I do say difficult but it is not impossible. If you have a
hematologist or hemoncologist who is willing to put fourth
the effort there are special dispensations available
through the FDA for the importation of unapproved drugs on
a compassionate use basis.
"Expanded access program (EAP). EAPs are typically designed
to provide widespread access to a drug that has proven
efficacy in clinical trials but is still awaiting FDA
approval. They’re similar to standard clinical trials with
a specific treatment plan and certain FDA requirements, but
they have looser patient eligibility criteria. More than
23,000 U.S. cancer patients enrolled in an EAP for Iressa
before it was FDA-approved, for example."
"Single patient use. This program offers an experimental
drug to an individual patient, rather than a group. The FDA
approves these uses on a case-by-case basis. Decisions are
based on other treatments already available and information
about the drug’s efficacy and potential toxicities."
http://www.curetoday.com/backissues/v3n3/departments/specialreport/index.html
To date I have no knowledge that anyone has sought any
single use or expanded access from the FDA for Nicosan.
Unfortunately regardless of the dissemination of this
information thus far no one has put forth the effort to
obtain the drug for use.
If just one person would start the ball rolling with a
caring and concerned medical practitioner it could open up
the drug for wide spread use by tens of thousands of
patients across the U.S. Unfortunately thus far the general
response I receive is that people don't believe that their
physician would be interested in going to this sort of
effort nor do they themselves seem to be inclined to seek
the use of a treatment that could potentially end their
crises.
There has to be at least one physician out there who has
enough care and concern for his patients to be willing to
put forth the effort necessary to obtain this medication
legally. I urge anyone who is effected by sickle cell to
approach their physicians with this information and attempt
to obtain this treatment not only for themselves but for
all patients who could potentially benefit from it's use.
We already know the benefits of the treatments available in
the U.S. and the E.U.. In many cases they are only
marginally effective or in the case of hydroxyurea cause
side effects so serious that many choose not to use it as
treatment. Here we have an opportunity to use a treatment
that has been shown to be highly effective, eradicating
crises in the majority of patients and reducing crises by
50% in the most refractory cases.
Although the clinical trial group was what the casual
reader might interpret as quite small it is common for
drugs which fall into the orphan drug category to use small
sample groups. Many orphan drugs have been approved based
on very small phase II and phase IIb clinical trials in the
U.S. In the case of FDA fast track status, a drug may be
approved during phase II trials if the drug shows
significant advantage over current approved therapies for
life threatening illness.
Fast Track Designation is a program that, if granted, is
designed to facilitate the development and expedite the
review of new drugs, thereby allowing the FDA to approve
drugs used to treat a serious condition or a
life-threatening disease with less safety data following
the conclusion of phase II studies, rather than phase III,
the normal practice.
The main criterion for a Fast Track Designated drug is the
potential to treat a life-threatening illness or fill a
major unmet medical need. Fast Track may be submitted with
the IND or at any time during the clinical development of
the drug. The Fast Track designation may allow a company's
application to follow Priority Review, Standard Review, or
a Rolling Review of the application.
http://www.fda.gov/CbER/gdlns/fsttrk.pdf
Nicosan by Western standards is an extremely inexpensive
drug. It is available in Nigeria without prescription at
$23/month for adults and child doses at $18/month.
Here is a link to the company and product website.
http://xechemnigeria.com/products.htm
I sincerely hope that you find this information helpful. I
would encourage you to to forward and post this information
to any person, blog or website where persons effected by
sickle cell anemia can have access to this information.
Feel free to write me with any questions or you may have.
NicosanForSickleCell@yahoo.com
Post a Comment