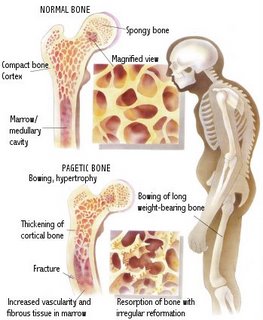
Disease of unknown origin. There is increased bone turnover due to an increase in bone osteoclast activity , which leads to increased osteoblast activity. Increased bone remodeling leads to bone enlargement, deformity and weakness.
Clinical presentations
Usually bone pain, bone deformity and deafness
Physical signs
You may notice bone deformity and warm bones. Rare in patients less than 40 years old. Rare as well in tropical countries.
Investigations
I notice that a lot of candidates have problems interpreting Calcium, phosphate, ALP in various conditions, I find this the following table useful,
Bone disease calcium Phosphate ALP
Paget’s Normal Normal ^^
Myeloma ^/Normal Normal unless fracture
Osteomalacia down down ^
Osteoporosis Normal Normal normal
Bone metastasis ^ ^/ normal ^
( It is even more confusing for hyperparathyroidism, I would cover that in future post)
Remember that level of ALP reflects osteoblast activity, therefore, if there is no new bone formation, ALP level would not be raised. This also explains ALP is high in growing children! On the other hand, level of urinary hydroxyproline reflects osteoclast activity, when there is breakdown of bone, the level would be raised.
Diagnosis
Based on typical x-ray appearance and raised AP with normal Calcium and phosphate

Coarse trabeculation and bony expansion
Complications
Nerve/ cord compression
Osteogenic sarcoma
Heart failure ( high output)
Treatment
Bisphosphonates is the treatment of choice. It inhibits bone resorption ( osteoclast activity) . It is also used in management of hypercalciamia especially in bone metastasis and osteporosis!
Tips for MRCP
Remember that patients with Paget's disease always have a raised ALP with normal calcium and phosphate !

1 comment:
Thanks for the update.There are many types of bone pains and diseases and it is essential to know which one exactly you are hit with. Plastic Surgeons Atlanta
Post a Comment