1) A 26-year-old male presents with 2 days history of diplopia and unsteadiness. 2 weeks ago he suffered from viral fever. Examination reviews that there is complete opthalmoplegia, areflexia and gait ataxia. Which of the following blood tests is the most likely to confirm the diagnosis?
1 ) Acetylcholine receptors antibodies
2 ) Anti GM1 antibodies
3 ) Anti GQib antibodies
4 ) Anti Topoisomerase antibodies
5 ) Anti purkinje cell antibodies
ANSWER: 3
2) A 40-year-old woman is referred with a two-week history of difficulty walking . On examination, there was distal limb weakness and the power is 3/5. Tendon reflexe was absent over ankle and the plantar responses were flexor.There was no sensory loss. What is the most likely diagnosis?
1 ) polymyositis
2 ) cervical cord compression
3 ) Guillain-Barré syndrome
4 ) myasthenia gravis
5 ) poliomyelitis
ANSWER: 3
3) A 50 year old female is admitted with progressive weakness following a flu-like illness. Which of the following would exclude Guillain-Barre Syndrome as the diagnosis?
1 ) Autonomic dysfunction
2 ) Elevated protein on CSF examination
3 ) Evidence of muscle wasting
4 ) Ophthalmoplegia
5 ) Sensory involvement
ANSWER: 5
4) A 15 year old girl presents with Guillain-Barre syndrome. Her weakness continues to worsen after admission to hospital and she complaines of shortness of breath. Which of the following should be used to monitor her?
1 ) arterial blood gases
2 ) chest expansion size
3 ) FEV1/FVC ratio
4 ) PEFR
5 ) vital capacity
ANSWER: 5
5) Which of the following clinical manifestations suggests Guillain Barré Syndrome?
1 ) Weakness beginning in the arms
2 ) Asymmetrical involvement of distal muscles
3 ) Bulbar involvement in about 50% of cases
4 ) Brisk tendon reflexes
5 ) Normal CSF protein
ANSWER: 3
6)A 43-year-old woman develops a progressive, ascending motor weakness over several days. She is hospitalized and requires intubation with mechanical ventilation. She is afebrile. A lumbar puncture is performed with normal opening pressure and yields clear, colorless CSF with normal glucose, increased protein, and cell count of 5/microliter, all lymphocytes. She gradually recovers over the next month. Which of the following conditions most likely preceded the onset of her illness?
1 ) Ketoacidosis
2 ) Staphylococcus aureus septicemia
3 ) Systemic lupus erythematosus
4 ) Viral pneumonia
5 ) Vitamin B12 deficiency
ANSWER: 4
7)Common features of normal pressure hydrocephalus are EXCEPT:
A papilloedema
B The opening pressure for lumbar puncture is normal
C gait apraxia
D incontinence
E cognitive impairment
ANSWER: B
8)A 60 year-old man presents with a 2 month history of progressive confusion, gait disturbance, and urinary incontinence. Examination reveals gait ataxia. CT brain done is as follow, lumbar puncture reveals normal CSF pressure and constituents. Which one of the following managements steps is likely to be most helpful?
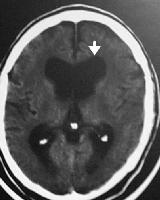
1 ) CSF drainage via repeated lumbar puncture
2 ) EEG
3 ) Intracranial pressure monitoring
4 ) MRI brainstem
5 ) Serum B12 and folate levels
ANSWER: 1
9)A 75-year-old man presented with an unsteady gait. He was noted to be becoming impaired with his memory and agitated at nights. His GP started an antidepressant. He was incontinent of urine. He was a heavy smoker and had lost 2 stones in weight over 2 months. His blood sugar was 10 mmol/l.
Which is the next best investigation?
1 ) CT Head
2 ) CXR
3 ) Arterial Blood gas
4 ) Thyroid function test
5 ) Blood Calcium level
ANSWER: 1

No comments:
Post a Comment