1) Acute haemorrhage appears to be hyperdense (white) in CT brain,
2) Chronic haemorrhage appears to be hypodense (black),
Condition 1: Cerebral toxoplasmosis

A few clues to the diagnosis,
1) Young patients with unexplained headache, fever,seizure,neurological deficit and increased intracranial pressure.
2) CTbrain shows ring enhancing lesion after IV contrast ( 30% unilocular but majority multilocular)
3) 75% at basal ganglia, occurs when CD4 less than 100.
Condition 2: Subdural Haematoma

Above image shows acute subdural haematoma ( white)
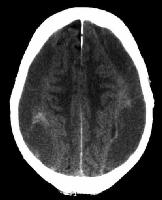 Above image shows chronic subdural haematoma (black)
Above image shows chronic subdural haematoma (black)
Usually in alcoholic and elderly patients. If it is acute, it appears to be hyperdense or lese it is hypodense in chronic lesion
Condition 3: Extradural Haematoma

Usually after motor vehicle accident or trauma. Remember about possibility of lucid interval.
Condititon 4: Stroke ( Ischaemic or Haemorrahgic stroke)
Simple to pick up in CT brain if it is massive, however, remember that CT scan may not have obvious changes in ischaemic stroke patients if less than 6 hours. ( Time required for the brain parenchyma to liquidfy after infarct to be shown in CT)
More photo based questions are coming...........

No comments:
Post a Comment