1)A 22 year old female who is 23 weeks pregnant is
seen in the outpatient clinic and noted to have
a sustained blood pressure of 170/92 mmHg. She
has no past medical history of note and has
otherwise been well and asymptomatic. This is
her first pregnancy. Urinalysis reveals protein (+) and
blood (+).
What is the most appropriate anti-hypertensive
therapy for this patient?
1 )ACE inhibitor
2 )alpha-Methyldopa
3 )Beta-blocker
4 )Hydralazine
5 )no treatment required
2)A 68 year old woman is admitted to hospital with
acute coronary syndrome and is discharged on day
5 after making a good recovery. She continues to
be under investigation of the cardiologists and
is discharged on atenolol 50 mg daily, enalapril
10 mg daily, isosorbide mononitrate 30 mg daily,
Atorvastatin 20 mg daily and aspirin 75 mg
daily. Her investigations at admission revealed
a serum urea concentration of 12.4 mmol/l with a
serum creatinine of 250 micromol/l. She is
re-admitted one week after discharge with
deteriorating dyspnoea. Investigations reveal a
serum urea of 34.9 mmol/l, a serum creatinine of
900 micromol/l, a serum bicarbonate of 12mmol/L
and a potassium concentration of 7.0 mmol/l with
tall tented T wave in leads over V2-6
What is the next plan of treatment?
1 )Calcium resonium
2 )Dialysis
3 )Insulin and dextrose infusion
4 )Sodium bicarbonate infusion
5 )Stop enalapril
3)A 27-year-old girl presented with a 4-day
history of severe back pain. A plain x-ray film
of her spine is normal. Two days later, she
complained of tingling in her fingers and toes.
The next day she became generally weak. She
presented in A/E.
On examination, she has bilateral leg weakness with power
3/5 , areflexia, flexor
plantars and normal sensation.
A lumbar puncture was performed and the CSF
analysis showed: Protein2.4 g/l (<0.4)
GlucoseNormal
Cells0
What is the most likely diagnosis?
1 )Botulism
2 )Guillain-Barre syndrome
3 )Acute poliomyelitis
4 )Myasthenia gravis
5 )Hysteria
4) In HIV disease, patients first become
susceptible to infection with Pneumocystis
carinii when the CD4 cell count falls to:
1 )<1000 cells/mm3
2 )<500 cells/mm3
3 )<350 cells/mm3
4 )<200 cells/mm3
5 )<50 cells/mm3
5)A 32-year-old male is followed up in the renal
clinic. His creatinine clearance (measured) is
76ml/min. A recent Ultrasound of his renal tract shows
enlarged kidneys bilaterally, with multiple
renal cysts. His father required dialysis at the
age of 45 years. On examination, his blood
pressure is 150/90 mmHg. Which of the following
statements is incorrect?
1 )An ACE inhibitor would be appropriate to
control his hypertension
2 )The risk of his children having the same problem is 50%
3 )Ciprofloxacin should be prescribed for upper
urinary tract infections
4 )Genetic counselling should be offered
5 )He should be informed of the probable need
for dialysis in 5-7 years
6)This patient presented to Casualty with acute
abdominal pain.
What is the diagnosis?
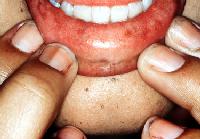
1)Peutz-Jegher's syndrome
2 )Crohn's disease
3 )Addison's disease
4 )Whipple's disease
5 )Porphyria cutanea tarda
7)A 52-year-old man was referred to the medical
outpatient clinic for assessment of fatigue. He
gave a four-month history of feeling 'tired all the time'. He had a past
history of hypertension that had been monitored
by his General Practitioner but this had not
required treatment. He had also reported feeling
in a 'low mood' to his GP, but attributed this
to the fatigue.
Investigations:
Hb14.9 g/dl
WBC8.1 x 109/l
Platelets179 x 109/l
MCV106 fl
Sodium132 mmol/l
Potassium4.0 mmol/l
Urea2.0 mmol/l
Creatinine110 µmol
Bilirubin28 µmol
Total protein69 g/dl
Albumin35 g/dl
Alk phos210 IU/l(NR 30-130)
AST98 IU/l(NR 20-40)
Gamma GT299 IU/l(NR <65)
9am Plasma cortisol877 nmol/l(NR 200-500)
12am Plasma cortisol 720 nmol/l (NR 55-250
nmol/l)
24-hour urinary free cortisol1120 nmol/l(NR
215-860)
What is the most likely underlying cause of
these abnormalities?
1 )Adrenal hyperplasia
2 )Alcohol
3 )Ectopic ACTH secretion
4 )Pituitary adenoma
5 )Depression
8)A 52 year old male presents with general
lethargy and abdominal swelling.
His symptoms have deteriorated over the last
three months and he denied long standing
heavy alcohol consumption but admitted that he was an intravenous drug abused.
Currently he is taking no medication and has no past history of
note. Examination reveals that he is well
orientated, is apyrexial and has a blood
pressure of 132/88 mmHg. He has numerous spider
naevi present on the upper chest and has
gynaecomastia. Abdominal examination reveals
tense ascites. He has splenomegaly on
abdominal examination. Investigations reveal:
Serum Sodium132 mmol/l (133-145)
Serum Potassium4.4 mmol/l (3.5 - 5)
Serum Urea 2.8 mmol/l (3 – 8)
Serum Creatinine135 micromol/l (50-100)
Bilirubin35 micromol/l (10-20)
AST 70 iu/l (10-40) Alkaline Phosphatase 220
iu/l (50-100) Albumin 25 g/l (35-45) Which of
the following measures would be most appropriate
in the initial management of this patient?
The following factors are the prognostic factor except
1 )Albumin
2 )INR
3 )Bilirubin level
4 )Presence of ascites
5 )Urea level
9)An 82-year-old gentleman is referred to your
outpatient clinic by his GP. He gives a two
month history of proximal muscle stiffness,
especially in the morning. He denies any
weakness.
What is the next best investigation?
1 )Plasma creatine kinase
2 )Muscle biopsy
3 )Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
4 )Antinuclear antibody
5 )Electromyography
10) These thyroid function tests were obtained from
a 60 year old male who presents with tiredness.
Past history includes ischaemic heart disease
and depression, for which he takes medication.
Free T4 25.7 pmol/l (NR 9.8 - 23.1 pmol/l)
Free T3 3.0 pmol/l (NR 3.8 - 5.8 pmol/l)
TSH 7.8 mU/l (NR 0.5 - 4.2 mU/l)
Which of the following is the most likely
explanation for these results?
1 )Amiodarone therapy
2 )Grave's disease
3 )Lithium therapy
4 )Sick euthyroid syndrome
5 )Subclinical hyperthyroidism
To check the answers, click here!

No comments:
Post a Comment